This first ran in Madeloud way, way back in 2009. So out of date, but hopefully still entertaining.
_________
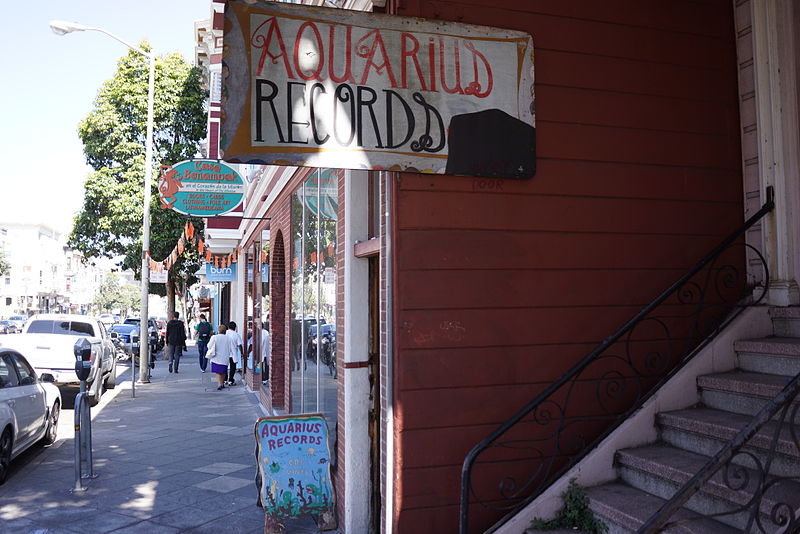

The Aquarius Records website is just about the most mind-bogglingly erudite font of esoteric music I could ever even imagine, much less witness. Every other week the store releases a massive 25,000-word-plus new arrivals list. They’ve published more than 300 of these monsters, and all are archived and accessible through their impressive search function. The result is a gargantuan, thorough, hysterical, learned, thoughtful mountain of obsessively cross-referenced prose about every kind of obscure metal, noise, psych, roots, electronica, funk, krautrock, shoegaze, and more. Store owner Andrew Connors (better known as aNDEE to AQ customers) spoke to me by email about the store and the list.
When did you start doing your reviews of new releases?
Not sure exactly. 10 years ago? We decided to start spreading the word about the store via short emails, original reviews were more like one sentence. If we were SUPER psyched about something maybe one paragraph, it was mostly for locals, to see what was new and come down and buy stuff. Eventually, people all over started signing up for our email list, and as it grew into a proper mailorder, the list sort of took on a life of its own, and the reviews blossomed into ESSAYS haha. I sometimes long for those one sentence days for sure. But folks love the list, and we do actually love writing it. And a lot of the stuff we sell and carry, is obscure enough that people might not check it out or give it a listen without the reviews. And in the store, we take those reviews and print them out and affix them to the cds, so people can come in, and it’s like a bookstore, with the little tags on each record, which hopefully makes browsing through all this crazy stuff, easier, and more interesting and fun.
How exactly do you compile these lists?
By the seat of our pants unfortunately. It just depends on what comes in, what gets released. Stuff we’ve been able to track down direct from bands and labels. We write about the stuff we have been most excited about. Sometimes we include old stuff we’ve always wanted to review, sometimes there’s some new release that folks are dying for, and maybe we’re not insanely psyched about it, but folks want to know what we think…
Everyone here writes reviews, regular readers of the list can usually discern who reviewed what, although it’s written in a collective voice, a very eclectic, weirdly varied voice, some folks write more than others. I tend to write about 40-50 reviews for each list, which comes out every other Friday. We all try to write them regularly, a few every day, bit more often than not, it gets right down to the deadline, and we’re scrambling to finish.
Do you review everything that comes into the store?
We get so much stuff, that would never be possible. New release wise, there are probably 100-200 every week, then cd-r’s and lps and 7″s submitted for review direct from bands and labels, another 50 or so every week? Just not enough time in the day. As it is, I try to listen to every single thing we get in, but it’s gotten harder and harder. As for how we decide, it really comes down to stuff we dig. The things we find ourselves listening to over and over and over. It’s very subjective, but it’s meant to be, we try to find the records we love and then champion them. I usually compare it to making a mixtape, the new arrivals list for me is like a massive mixtape we make for our friends every two weeks, stuff so good you want other people to hear it and love it, and hopefully buy it.
Do you feel that the lists are worth the effort in terms of sales?
Absolutely. It’s one of the things that defines our store. And unlike most stores, we have this list that people who live thousands of miles away can read, and feel like they’re a part of. We try to make it fun and friendly and interesting to read, our regular mailorder customers generally become friends of ours, when they visit here we hang out, when we’re traveling we end up meeting and sometimes staying with mailorder customer. It functions the way record stores have traditionally functioned, building a sense of community, cuz sure this is a business, but there’s not much money to be made, if we wanted to get rich, we sure as hell would be doing something else, but we LOVE music, as do the people who read the list, which for me, DOES make it good business, even just on that level, music nerds obsessing about new records and new bands and crazy sounds, and because of that, it does in fact generate much of our business, people anxiously await friday night to see what new stuff showed up and to order a bunch of cool crazy music.
It is a lot of work, and of course sometimes we wish, we didn’t have a list to send out, it certainly affects how we live our lives, when we can go away, how long we can go away, our days off, the way we feel about music, knowing that if we like something, we’re also gonna have to review it, but I definitely think it’s something super special, and I hope other folks feel the same way.
Looking at these lists online, you sort of get the feeling that the store itself must be gigantic. How big is the store? How many records do you have in stock at one time?
That’s funny. It really does. And I sometimes feel bad when someone finally gets to visit, having come all the way from Japan or the UK, I feel like we should apologize for how small the store is, but almost always, people dig it. It’s small-ISH, but there’s tons of records, cds, plants in the windows, posters and flyers, and crap all over the walls, doors and posts and windows have been painted by artists, there are video games (a Tron, a Rastan and a Joust, and we usually have a Ghosts And Goblins, but that one’s broken), there’s good music playing, it’s just really comfortable and worn and home-y, the way a record store should be.
As for how many records we have in the store, only a fraction of what’s on the website. we’re usually full to capacity, but the cool thing about visiting is, there’s always plenty of stuff that is NOT on the site, maybe stuff we haven’t reviewed yet, stuff that we were only able to get a few copies, not enough to post on the site, some stuff that just won’t make it on the site, for whatever reason, not to mention TONS of awesome used stuff, and new arrivals and more…..
What would you say is your favorite review on the site?
One of my favorites is probably for the M83 record, when we first heard them, mostly for the last couple sentences:
“Now imagine [the album] as the soundtrack to the love scene in some super bizarre Anime. You know, the part where the girl is going into space because she can’t live on earth because her tentacles keep killing cute little pandas, and her boyfriend is a giant panda, but they love each other so much her tears turn into jewels that the pandas can eat to make them invincible. It’s that heartbreakingly good.”
What releases are you looking forward to in the next few months?
Definitely excited about the new Velvet Cacoon, long time aQ faves, a band from Portland who do a super blissed out fuzz drenched eco black metal. REALLY PSYCHED on the forthcoming Teenage Filmstars reissues, one of THE best heavy druggy shoegaze bands EVER. Some of us think WAY better than My Bloody Valentine (I know, blasphemy! haha), the new Bunkur, killer crushing slow motion ultra doom from Holland, the new Yoga, super tripped out murky droney sort-of-black metal, and also pretty excited for the new Arctic Monkeys…. and sure there will be more more more!!









![Felipe Hernandez Cava (w), Federico del Barrio (a), Lope de Aguirre, La conjura [Lope de Aguirre, the conspiracy], Ikusager, 1993.](https://www.hoodedutilitarian.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/Aguirre-227x300.jpg)
![Stefano Ricci, La storia dell'Orso [the bear's story], Quodlibet, 2014.](https://www.hoodedutilitarian.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/Orso-1-269x300.jpg)